The importance of learning thermodynamics and heat transfer for D4 Automotive Engineering Technology
tro.vokasi.unesa.ac.id - Thermodynamics and heat transfer are crucial for D4 (Diploma IV) Automotive Engineering Technology because they are the foundational principles that govern how a vehicle's engine and its related systems function. Understanding these subjects allows a student to move beyond a simple "how it works" to a "why it works" and "how to make it work better" mindset.
Thermodynamics: The "Why" and "How Much"
Thermodynamics focuses on the relationships between heat, work, and energy. For an Automotive Engineer, this is essential for:
1. Engine Cycles
You'll learn about thermodynamic cycles like the Otto cycle (for gasoline engines) and Diesel cycle (for diesel engines). Understanding these cycles is key to analyzing how fuel energy is converted into mechanical work to move the vehicle. It helps in calculating the theoretical maximum efficiency of an engine.
2. Fuel Efficiency and Performance
The principles of thermodynamics, particularly the first and second laws, are used to design and optimize internal combustion engines for better fuel efficiency and power output. This includes analyzing the combustion process to maximize the work produced from the chemical energy in the fuel.
3. Alternative Powertrains
The principles extend beyond conventional engines. In electric and hybrid vehicles, thermodynamics is used to analyze energy conversion in batteries, electric motors, and even in waste heat recovery systems.
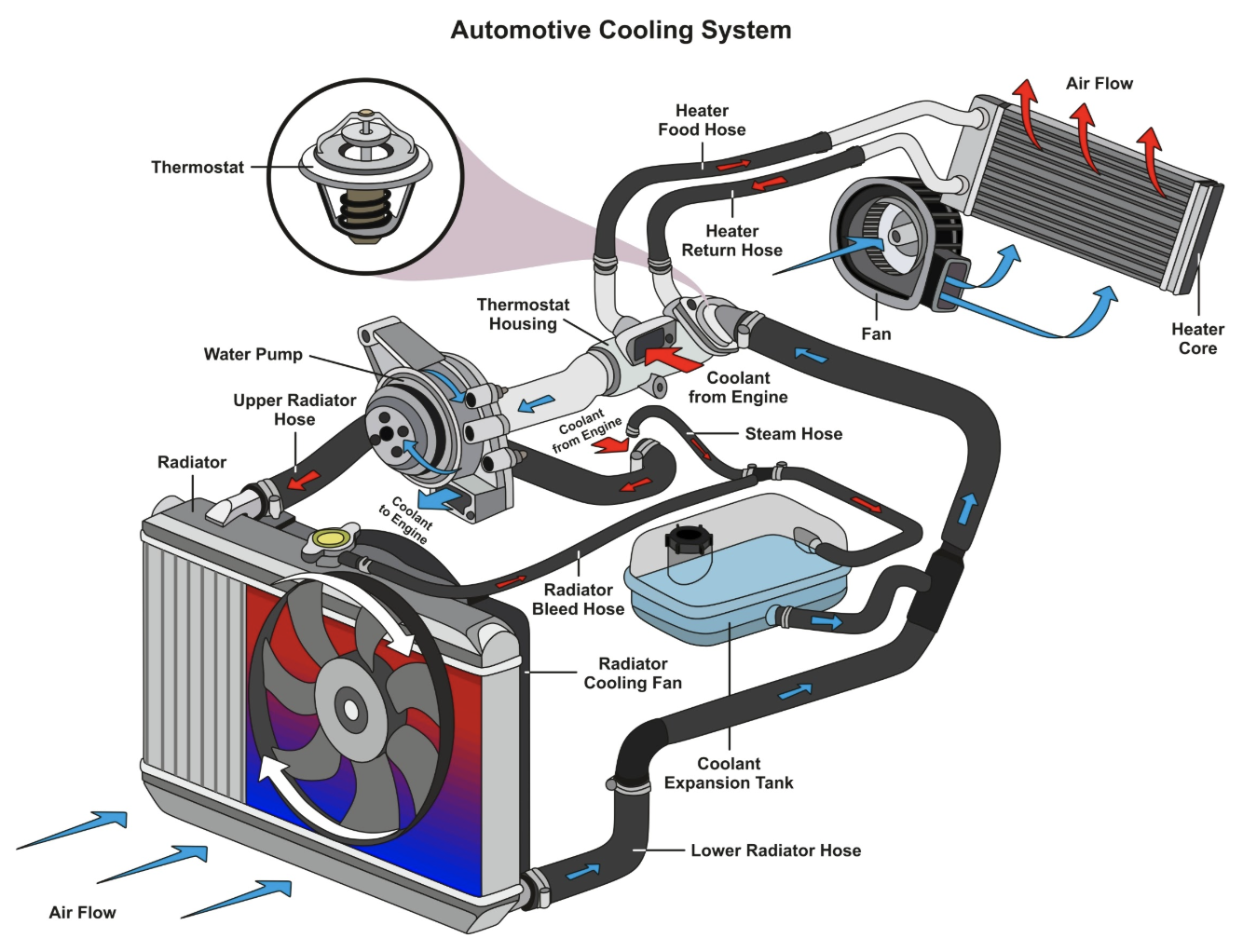
Heat Transfer: The "How Fast" and "How to Manage"
Heat transfer deals with the rate at which heat moves from one place to another. This is a critical practical application in automotive technology for :
1. Engine Cooling Systems
Engines generate a tremendous amount of heat. Without a proper cooling system, they would quickly overheat and fail. You'll use heat transfer principles to design and analyze cooling systems, radiators, and fans to ensure the engine operates at its optimal temperature.
2. Thermal Management
This applies to almost every part of a car. You'll learn how to manage heat in the exhaust system, braking systems, and even in the vehicle's climate control (AC) system. For electric vehicles, thermal management of the battery pack is vital for its longevity and performance.
3. Material Selection
Understanding heat transfer helps in selecting the right materials for different components. For instance, you need to choose materials with good thermal conductivity for engine blocks and radiators, and materials with low thermal conductivity (insulators) for protecting sensitive components from excessive heat.
-
In conclusion, a strong grasp of thermodynamics and heat transfer is essential for any aspiring automotive engineer. These fields are not just theoretical concepts; they are the fundamental tools used to design engines, manage energy, and ensure the performance and longevity of every vehicle on the road, from traditional internal combustion engines to the latest electric powertrains.
Class of 2025 A - Thermodinamics